Collecting 1.8M news documents from Common Crawl
2 Months ago, I trained a tiny language model with 10M parameters on turkish news datasets [1]. However, 10M parameters turned out to be not enough to generate good news articles. Following the Tiny Stories[2] paper, I decided to train a larger network, a network with 30M parameters. A larger network needs more training data. In this article I will explain how I collected 1.8M news documents from Common Crawl.
Code[18] and Dataset[21] is available.
How to obtain data from common crawl
Common Crawl is the most obvious source to collect web pages. However, common crawl dumps are huge that requires petabytes of storage which something I don’t have. Instead of downloading CC dumps and scanning for news articles in the dump, I decided to use a different approach.
I decided to find list of URLs to download beforehand. So that I do not need to download all CC dumps. I only need to download CC dumps with news articles I am looking for.
Common Crawl index service[3] can be used to fetch list of URLs belonging to a web-domain. But it turns out, even downloading CC dumps containing the URLs I am interested in requires a lot of storage.
Common Crawl index service provides data in CDX[4] format. CDX format comes with offset and length fields that can be used to fetch a specific range of bytes from the file. So it is possible to download relevant chunks from the CC dumps without downloading the whole file.
Selecting web-domains
Some outlets have similar tone and similar selective bias on selecting topics. So it is important to select domains with diversity in mind.
Once web-domains are selected, CDX Index client[5], authored by Ilya Kreymer, lead maintainer of Common Crawl, can be used to fetch URLs belonging to a web-domain.
Not all URLs are news articles
Some URLs are not news articles. For example, some URLs belonging search results are not news articles. Some of the URLs belong to labels and categories that can be used to navigate the web-site.
I wanted to exclude non-news pages from training data.
In the beginning, I analyzed all URLs belonging to a domain to find heuristic rules to determine which URLs are news articles which are not. This approach worked well but obviously was not scalable. I still collected some data with this approach.
I used the collected data [6] to train a classifier to automate the process.
First I decided to go with a BERT based classifier. After experimenting with several architectures I decided to go on with distilbert. I finetuned a distilbert model [7] using the classification dataset I created. Accuracy on test set was above 96% which was quiet good. I created a fastapi based server for batch inference on the trained model[8]. However, distilbert, despite being a fast bert model, was not fast enough for classifying thousands of urls.
After, additional experiments, I realized bert model was not using content of html text for classification, it was only using metadata. It turns out metadata being used was canonical URLs found in link tags. Then, I decided to use a ML based classifier to do classification on the URLs. After trying with several different algorithms, I finally settled on Support Vector Machines(SVM)[9]. Accuracy was above 94% which was quite good. And it was blazing fast.
At the and SVM turned out not to generalize well for the task. I stopped iterations on the classifier. Trying URL classification with distilbert seemed promising but i did not try it. Because I noticed most of the non-news pages were filtered out at the filtering phase.
I inspected filtered documents and found out that most of the non-news pages were missing. I added an additional filter and measured precision. Precision was above 99% which was quite good. As a result, I abandoned the classification component. The drawback is I need to download all pages and process them until the filtering phase.
Downloading Chunks
Downloading thousands of chunks from Common Crawl is a long running task, in the mean time many things can go wrong. It is important to keep track of the progress to avoid starting from scratch in case of faults. I experimented with many alternatives and decided to go on with the following approach.
CDX Index is loaded to an sqlite db. Downloading script takes a small batch of urls from the db table, e.g. 1000, and downloads them in parallel. Parallelism is limited to 30 concurrent items to avoid hitting the CC servers with too many requests. Once all urls from the batch is downloaded, html contents are saved to a JSON (*.jsonl) file named using the smallest id of rows in the batch. Then rows are updated in the db to mark them as completed, either as success or failure.
If download process halts for some reason, only the incomplete batch with 1000 rows is retried in next launch.
Extracting text
Trafilatura[20] is used to extract text from html pages. Previously I was extracting Markdown from the html pages. However, Llama 3 paper[10] showed that Markdown is not a good input for language models trained on web data. So I decided to extract text from html pages.
Once text is extracted, it is filtered using filters from Datatrove[12]. The filters used can be see in [11]. Filters are applied per domain wise.
Deduplication
News articles explaining an event are typically published in multiple news outlets. Some outlets simply copies from other outlets. Sometimes, even the same article published multiple times in the same domain. Deduplication is a necessary step to avoid duplication. I experiment with pure minhash based deduplication[13], LHS with Jaccard index deduplication[14] and finally settled with LHS without any Jaccard index [15,16] calculation that is implemented in Datatrove[12].
Deduplication script can be seen in [17]. Deduplication is applied per domain and after combining all domain texts. First deduplication is essential for removing duplicates early on. Second deduplication step is essential for removing duplicates among domains.
450 buckets and 20 hashes per buckets are used. A document signature contains 9000 hashes, as in [15,16].
Results
Total of 3M (3,068,443) web pages were downloaded belonging to 10 different outlets(or web-domains).
- 79K articles were dropped during text extraction, for reasons not clear to me. A small part of them was due to the fact that text extraction was not complete within the time out period of 1 second. Rest of them is not clear.
- 381K articles were dropped after applying Gopher Repetition filter.
- 310K articles were dropped after applying Gopher Quality filter.
- 239K articles were dropped after applying FineWeb Quality filter.
- 142K articles were dropped after applying in-domain deduplication.
- 68K articles were dropped after applying cross-domain deduplication.
After all filtering steps, 1.8M (1,845,941) documents remained, which is 60% of the initially downloaded documents.
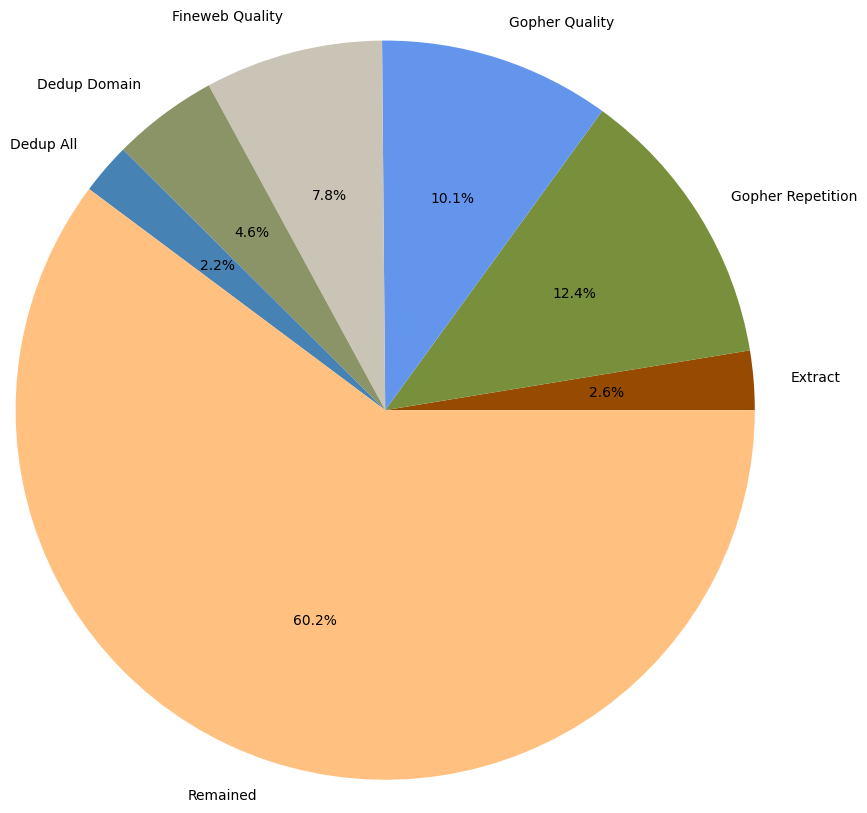
I was expecting to see more documents dropped at stage cross-domain deduplication, but it seems that this is not the case. While I see this suspicious, there are no additional indicators to believe it is not correct.
Conclusion
1.8M documents can be used to train a small GPT-2 model. e.g. 30M parameters. Since the pipeline is ready, it is possible to collect more documents and train larger models. The beauty of this pipeline is that it runs with a low resource footprint. I run all the steps in my notebook with 8 (4 virtual) cores and 32GB RAM. But datatrove library, our pipeline is based on, can run on multiple machines, which makes the whole process really scalable.
Whole code of the pipeline is open source and available at [18] with name cc-spider.
Whole dataset is available at [21] with name news-tr-1.8M.
Finally I can start training HaberGPT-2 model using my training script[19].
References
2- Tiny Stories
4- CDX Internet Archive Index File
6- News Classification Dataset
11- Filtering Script
12- Datatrove
13- Scalable Minhas
18- CC Spider
20- Trafilatura