Granite Foundation Models
Paper provides details about data used in pre-training phase.
DATA SOURCES
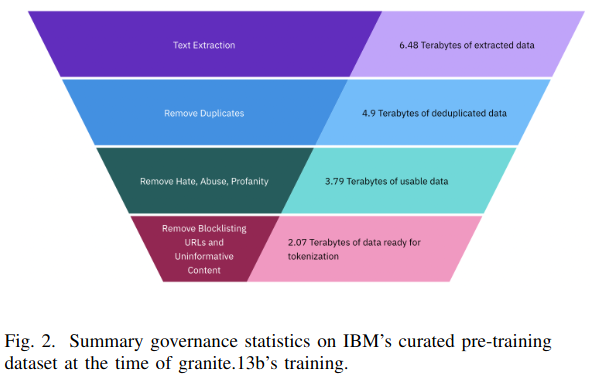
- 6.48 TB of data before pre-processing,
- 2.07 TB of data after pre-processing.
- Unstructured English-text and code.
- All non-text artifacts (e.g., images, HTML tags, etc.) were removed.
- granite 13b trained on 1T tokens out of 14 datasets.
Data sets:
- arXiv: Over 1.8 million scientific paper pre-prints posted to arXiv.
- Common Crawl: Open repository of web crawl data
- DeepMind Mathematics: Mathematical question and answer pairs data.
- Free Law: Public-domain legal opinions from US federal and state courts.
- GitHub Clean: Code data from CodeParrot covering a variety of coding languages.
- Hacker News: News on computer science and entrepreneurship, taken between 2007-2018.
- OpenWeb Text: Open-source version of OpenAI’s Web Text corpus containing web pages through 2019.
- Project Gutenberg (PG-19): A repository of free e-books with focus on older works for which U.S. copyright has expired.
- Pubmed Central: Biomedical and life sciences papers.
- SEC Filings: 10-K/Q filings from the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for the years 1934-2022.
- Stack Exchange: Anonymized set of all user-contributed content on the Stack Exchange network, a popular collection of websites centered around user-contributed questions and answers.(see [2] as a possible source)
- USPTO: US patents granted from 1975 to May 2023, excluding design patents.
- Webhose: Unstructured web content converted into machine-readable data feeds acquired by IBM.
- Wikimedia: Eight English Wikimedia projects (enwiki, enwikibooks, enwikinews, enwikiquote, enwikisource, enwikiversity, enwikivoyage, enwiktionary). containing extracted plain text from pages and articles.
DATA GOVERNANCE
Data Clearance and Acquisition
A dataset is accepted after a completing a formal process involving data license, usage restrictions and sensitivty. Paper remarks that books3 dataset is excluded due to copyright concerns.
Pre-Processing Pipeline
- Text Extraction: Extract text from a document into a standard format.
- Data De-Duplication: Remove duplicate data per-dataset basis. exact de-duplication is hash based. fuzzy de-dupliction is finds Jaccard similarity between documents with locality sensitive hashing.
- Language Identification: Detect dominant language in a document.
- Sentence Splitting: Split documents into sentences. This step is necessary for HAP (Hate, Abuse, Profanity) annotation step.
- Hate, Abuse and Profanity Annotation: A HAP detector is used to assign score to each sentence.
- Document Quality: A classifier (based on KenLM linear classifier pre-trained on Wikipedia documents) and a heuristic (Gopher Quality Filtering criteria) is used to generate a quality annotation.
- URL Block-Listing: The Block list isincludes URLs of known copyrighted material as well as block-listed sites such those contained in the 2022 Review of Notorious Markets for Counterfeiting and Piracy.
- Filtering: Previously generated annotations are used to determine whether to keep or filter the document.
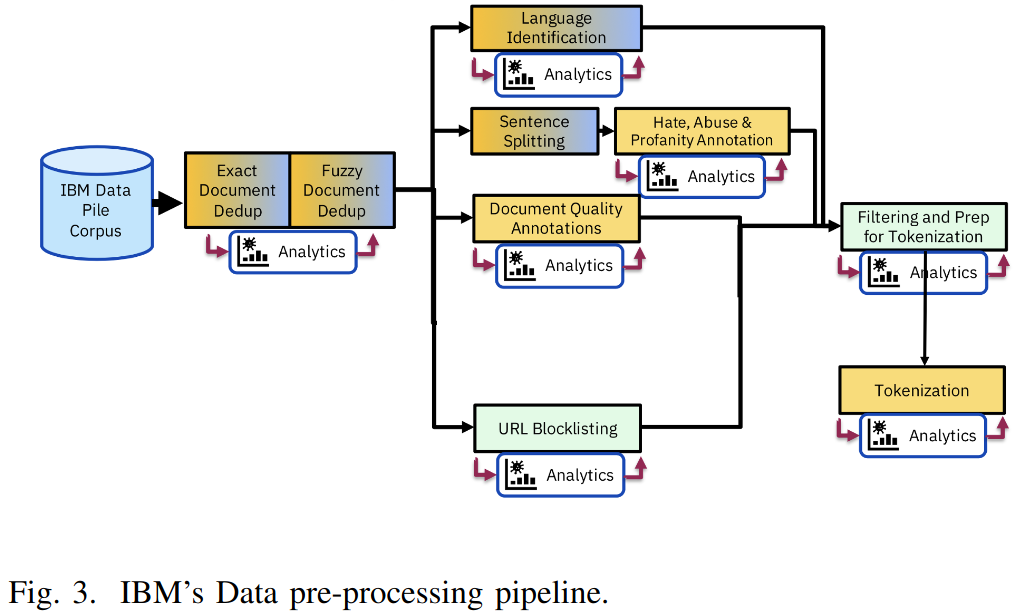
Tokenization
GPT-NeoX 20B tokenizer is used.
Training
Algorithmic Details
Pre-Training
granite.13b base model:
- Gaussian error linear unit (GELU) activation function
- MultiQuery-Attention for inference efficiency
- learned absolute positional embedding
- FlashAttention to speed up the training and reduce its memory footprin
- 300K iterations, with a batch size of 4M tokens, for a total of 1 trillion tokens
- Adam optimizer [24], with β1 = 0.9, β2 = 0.95, ϵ = 10−8, and a weight decay of 0.1
- cosine learning rate schedule, with warmup of 2000 steps, and decay final learning rate down from 3 × 10−4 to 3 × 10−5
- 3D-parallel layout using both tensor and pipeline parallelism including sequence parallelism to enable training with 8K context length
Supervised Fine-Tuning
granite.13b.instruct:
- cosine learning rate schedule with an initial learning rate of 2 × 10−5, a weight decay of 0.1
- a batch size of 128, and a sequence length of 8192 tokens.
SFT data includes:
- a subset of the Flan Collection
- 15K samples from Dolly
- Anthropic’s human preference data about helpfulness and harmlessnes
- Instructv3
- internal synthetic datasets specifically designed for summarization and dialogue tasks
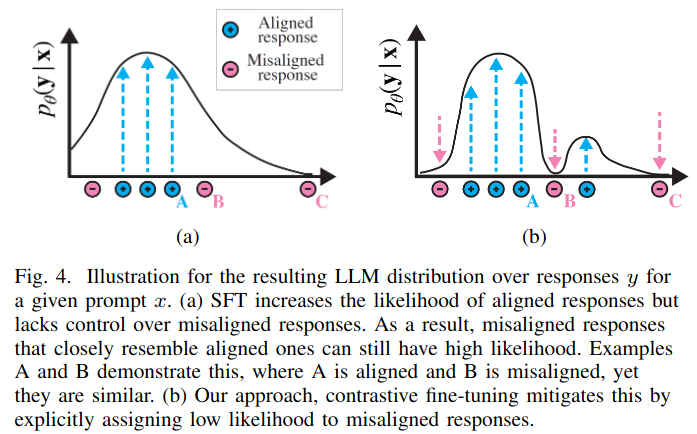
Contrastive Fine-Tuning
granite.13b.chat:
The paper proposes a contrastive alignment strategy which is call contrastive fine tunning (CFT) . To obtain negative examples, a separate LLM that is based on an early version of granite.13b.instruct which is fined-tuned on misaligned human datasets is used.
CFT dataset is based on:
- samples from Anthropic’s human preference data about helpfulness and harmlessness that have been filtered using the OpenAssist reward model
- samples from Dolly [2], and
- samples from ProsocialDialog

Compute
Granite.13b used 256 A100 GPUs for 1056 hours and 120 TFLOPs.
TESTING AND EVALUATION
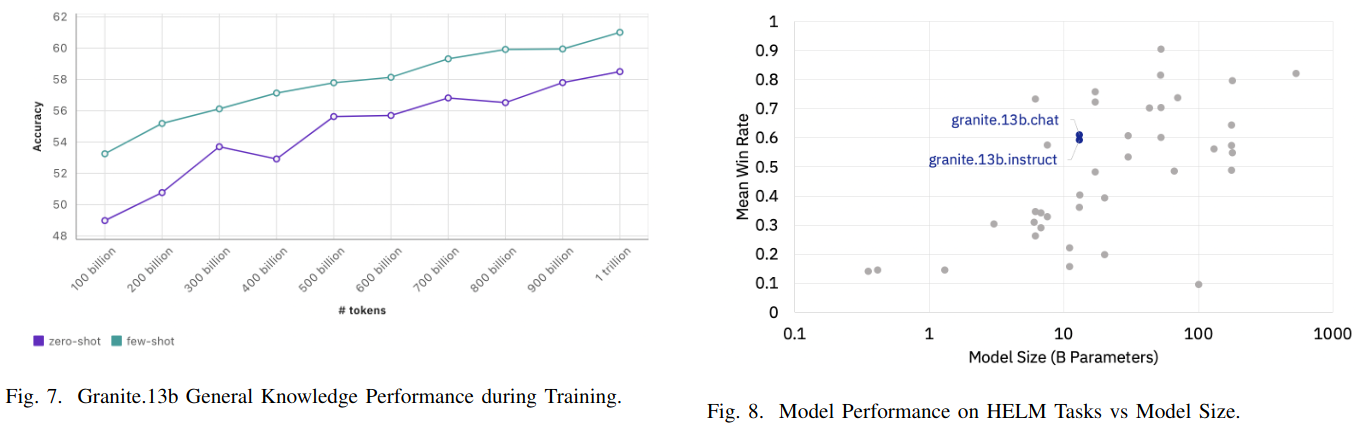
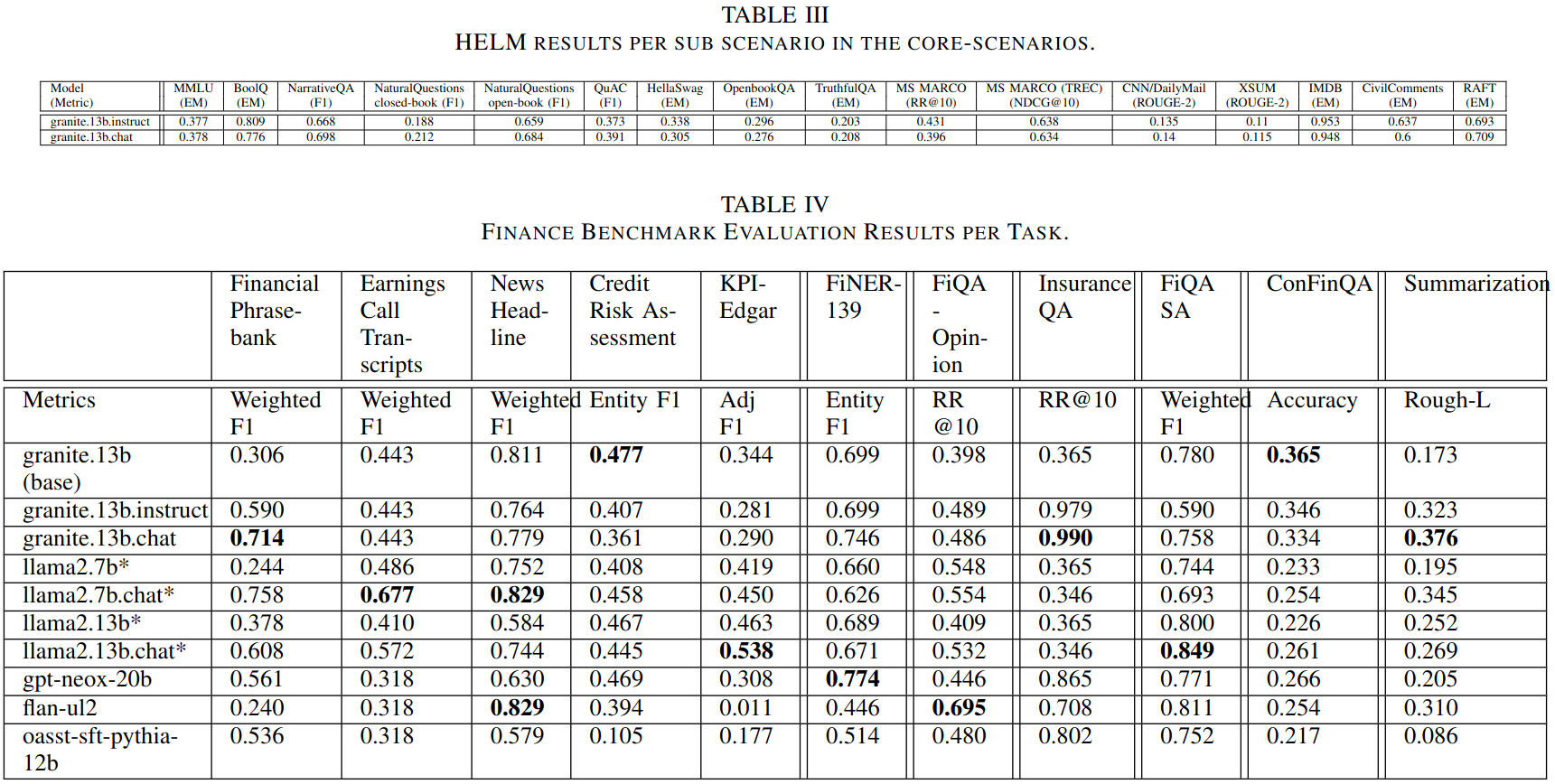
General Knowledge Benchmarks During Training
Includes a subset of Eleuther AI’s Language Model Evaluation Harness (lm-eval). used as light-weight tests run after every 100 billion tokens during training to validate model knowledge is advancing as training progresses
The following 12 datasets from lm-eval are used both in zero and few shot settings:
- question answering for several domains (boolq, open-bookqa, piqa, sciq);
- sentence completion (lambada)
- commonsense reasoning (arc easy, arc challenge, copa, hellaswag, winogrande);
- reading comprehension (race)
- multidisciplinary multiple-choice collection (mmlu)
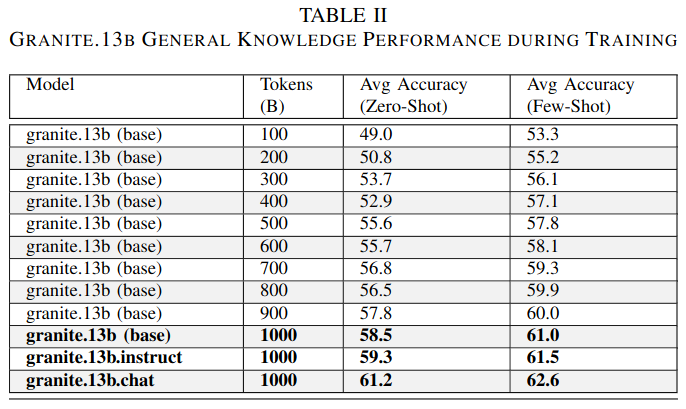
HELM
After pre-training is complete, a more comprehensive assessments relies on Stanford’s Hollistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM) Benchmark.
Enterprise Evaluation Benchmarks
After training completes, we further evaluate our models on IBM-curated enterprise benchmarks to test our models performance in domains relevant to potential customers. IBM curated 11 publicly available finance benchmarks for evaluating models in the financial domain.